COMPUTONE CORPORATION
INTELLIPORT II ISA-4R VER.1
|
Card Type |
Serial card |
|
Chipset Controller |
Computone |
|
I/O Options |
Serial port (4) |
|
Maximum DRAM |
N/A |

|
CONNECTIONS | |||
|
Purpose |
Location |
Purpose |
Location |
|
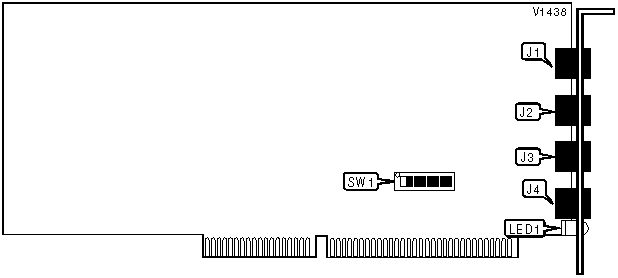
RJ-45 serial connector |
J1 |
RJ-45 serial connector |
J3 |
|
RJ-45 serial connector |
J2 |
RJ-45 serial connector |
J4 |
|
BASE I/O ADDRESS SELECTION | |||||||
|
Address |
SW1/1 |
SW1/2 |
SW1/3 |
SW1/4 |
SW1/5 |
SW1/6 |
SW1/7 |
|
158h |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
|
160h |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
On |
On |
|
168h |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
On |
Off |
|
170h |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
Off |
On |
|
178h |
On |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
|
3D8h |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
On |
Off |
Off |
|
3E0h |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
On |
On |
|
3E8h |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
On |
Off |
|
3F0h |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
On |
|
3F8h |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
Off |
|
Note: A total of 81 base address settings are available. The switches are a binary representation of the decimal memory addresses. SW1/7 is the Most Significant Bit and switch SW1/1 is the Least Significant Bit. The switches have the following decimal values: SW1/7=512, SW1/6=256, SW1/5=128, SW1/4=64, SW1/3=32, SW1/2=16, SW1/1=8. Turn off the switches and add the values of the switches that are off to obtain the correct memory address. (Off=1, On=0) | |||||||
|
BASE I/O ADDRESS BUS CONFIGURATION | |
|
Setting |
SW1/8 |
|
16-bit |
On |
|
8-bit |
Off |
|
DIAGNOSTIC LED(S) | |||
|
LED |
Color |
Status |
Condition |
|
LED1 |
Green |
Fast blink |
Card is performing memory diagnostic |
|
LED1 |
Yellow |
Slow blink |
Controller is waiting for firmware to download |
|
LED1 |
Yellow |
Fast blink |
Controller is downloading driver |
|
LED1 |
Green |
Slow blink |
Card is operating properly |
|
LED1 |
Red |
On |
Error code follows |
|
Note: If the LED blinks red, the blinks that follow indicate an error code. Yellow blinks are worth 1, and green blinks are worth 10. Add the values together to get the correct error code. | |||
|
ERROR CODES | |
|
Code |
Description |
|
1 |
Bad FIFO. Full/empty flags cannot track the state of the FIFO correctly; internal registers are bad. |
|
2 |
Bad DRAM. Expansion moduleís on-board DRAM failed random-pattern test. |
|
3 |
Bad Checksum Sensed During Download. FIFO may be unreliable or loadware file may be corrupted. Reinstall the loadware file & reboot system. |
|
4 |
Product ID is invalid. |
|
5 |
Dead UART. 1400 UXART is not responding correctly to a reset. |
|
6 |
Bad Mailbox. FIFO mailbox failed. |
|
7 |
Not used. |
|
8 |
Not used. |
|
9 |
Invalid Interrupt. CPU received an unexpected interrupt vector. The cause may be bad DRAM, a software problem, or a internal CPU problem. |
|
10 |
Bad First Command From Host. (1) The Set Interrupt Level command was not the first command received after writing the loadware. (2) An invalid interrupt request. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
11 |
Zero Count Data Packet. Data packet from host had a zero count. |
|
12 |
Invalid Command Number From Host. A packet received from the host had a command # that is out of range (too big). This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
13 |
Bad Synchronous Command From Host. A synchronous packet received from the host had a command # that is only valid in a bypass packet, or an unassigned command was sent. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
ERROR CODES (CONíT) | |
|
Code |
Description |
|
14 |
Internal Software Check. The dss_enable ( ) command was called with one or more illegal arguments. This may indicate bad DRAM or a problem with loadware. |
|
15 |
Empty Data Packet. Line discipline task received a packet with no data. |
|
16 |
Not used. |
|
17 |
Internal Software Check. The list of running tasks may be bad. This may indicate bad DRAM or a problem with loadware. |
|
18 |
Bad Bypass Command From Host. A bypass packet received from the host had a command # that is only valid in a synchronous packet, or an unassigned command was sent. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
19 |
Internal Software Check. Table full; unable to spawn a new process. This may indicate bad DRAM or a problem with loadware. |
|
20 |
Internal Software Check. The process stack has overflowed. This may indicate bad DRAM, a problem with loadware, or a problem with the interrupt. |
|
21 |
Internal Software Check. A transmit interrupt was received while processing a send break command. This may indicate a bad 1400 UXART or a problem with the loadware. |
|
22 |
Incoming Data or Command Overflow. The host has sent to much commands or data than the controller has room for, in violation of the driver & the loadware. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
23 |
Change # Too Large. The host sent a packet to a channel # higher than the maximum channel # for the controller. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
24 |
Not used. |
|
25 |
Unexpected UART Shutdown. The UART transmitter has shutdown for an unknown reason. |
|
26 |
Not used. |
|
27 |
Stuck Mailbox-Interrupt Bit. The controller received a (mailbox) interrupt from the host. When servicing the interrupt , the mailbox interrupt bit was clear. This may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
28 |
Dead UART. One of the 1400 UXART is not responding to a reset. This may show a bad 1400 UXART or a problem with the loadware. |
|
29 |
Unsupported Product. (Loadware Ver. 1.0.2 or earlier). Loadware was used on an Intelliport II EX, but is used for the Intelliport II only. |
|
29 |
Internal Software Check. (Loadware Ver. 1.0.3 or earlier). LCD process could not be started. |
|
30 |
No Expansion Modules Connected. No expansion modules are connected to the Intelliport II EX. Shut down the system & connect the expansion modules. |
|
31 |
Reserved. For development /debugging. If this code appears, it may show bad DRAM or software problem. |
|
32 |
Invalid Channel #. The host sent a packet that does not exist. his may show an unreliable FIFO, or a problem with the driver or loadware. |
|
33 |
Bad Buffer Pointer. A buffer head pointer is not word aligned. |
|
34 |
Bad Buffer Pointer. A buffer head pointer is not word aligned. |